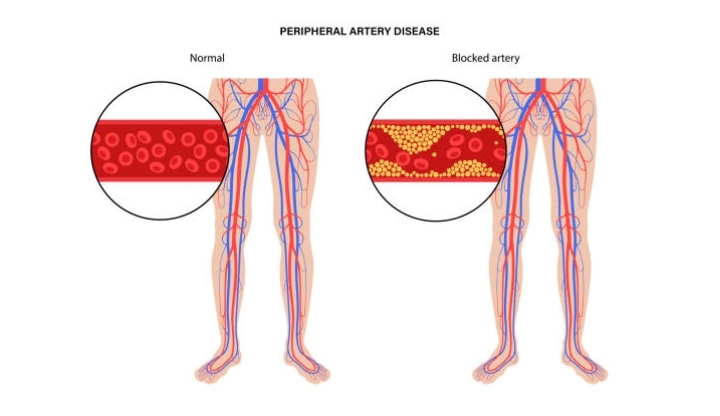
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a common yet serious circulatory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the arteries that supply blood to your limbs, particularly the legs, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of fatty deposits, or plaque. This restriction in blood flow can lead to a range of symptoms, including leg pain when walking, numbness, and, in severe cases, tissue damage. Understanding PAD is crucial for managing the condition and improving long-term outcomes.
What is Peripheral Arterial Disease?
Peripheral Arterial Disease is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, the process of plaque building up on the inner walls of the arteries. This plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, limiting the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your muscles and tissues. While PAD most commonly affects the legs, it can also impact the arteries that supply blood to the arms, stomach, and head.
The symptoms of PAD depend on the severity of the disease. Some people may experience mild or no symptoms at all, while others may suffer from:
- Claudication: Pain or cramping in the legs or hips during walking or exercise, which usually subsides after a few minutes of rest.
- Numbness or weakness: Reduced blood flow can cause your legs to feel weak or numb.
- Coldness in the lower leg or foot: The affected limb may feel colder than the rest of your body.
- Poorly healing sores or wounds: Reduced circulation can prevent injuries from healing properly, leading to the risk of infection and complications.
- Discoloration of the skin: The skin on your legs or feet may change color, becoming pale, blue, or shiny.
Will Peripheral Arterial Disease Adversely Impact My Life?
The prognosis of peripheral arterial disease varies widely depending on several factors, including the severity of the condition, the presence of other health issues, and how well the disease is managed. While PAD itself is not typically a direct cause of death, it is a serious condition that significantly increases the risk of life-threatening complications, particularly arterial events such as heart attacks and strokes. If left unchecked, it can also affect your quality of life.
1. Arterial Disease: One of the most concerning aspects of PAD is its strong association with arterial disease. The same atherosclerotic process that causes PAD can also affect the arteries that supply blood to the heart and brain. As a result, individuals with PAD are at a significantly higher risk of heart attack, stroke, and other arterial events. In fact, the presence of PAD is often considered a marker for widespread atherosclerosis, indicating that other arteries in the body may also be affected.
2. Limb Complications: In advanced stages, PAD can lead to critical limb ischemia (CLI), a severe form of the disease characterized by severe pain, non-healing wounds, and tissue death (gangrene). CLI significantly increases the risk of limb loss through amputation. However, with timely intervention, including revascularization procedures that restore blood flow, the risk of amputation can be reduced.
3. Management and Treatment: The good news is that PAD can be managed effectively with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, adopting a healthy diet, and engaging in regular exercise, can significantly improve symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Medications to control blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar (in diabetics) are also essential components of managing PAD.
Early intervention can also slow down disease progression and reduce complications of the disease. In some cases, minimally invasive procedures such as angioplasty or stenting may be necessary to open up narrowed arteries and restore blood flow. For those with severe PAD or critical limb ischemia, surgical interventions such as bypass surgery may be required.
To learn more about the treatment options available and how they can be tailored to your specific needs, consider exploring our arterial care strategies, which focus on both prevention and intervention.
Improving the prognosis of PAD
While PAD is a serious condition, it does not signal the end of your quality of life. With proper management, individuals with PAD can live long, active and enjoyable lives. Here are some key strategies for improving the prognosis of PAD:
- Regular Monitoring: Routine check-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial for monitoring the progression of PAD and managing risk factors. This includes regular blood tests, blood pressure monitoring, and imaging tests such as ultrasound to assess blood flow in the arteries.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to improve your arterial health. Additionally, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help manage cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Regular exercise, such as walking, can also improve circulation and reduce the symptoms of claudication.
- Medications: Taking prescribed medications as directed is essential for managing PAD and reducing the risk of complications. This may include antiplatelet medications to prevent blood clots, statins to lower cholesterol, and medications to manage blood pressure and diabetes.
- Interventional Procedures: For those with more severe PAD, interventional procedures such as angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow and prevent complications. Salvage therapy such as deep venous arterialization can also be offered for select patients who have not responded to other treatment options. Dr. Darryl Lim is one of the few surgeons who can perform deep venous arterialization in Asia.
For more detailed insights into how we approach the management and treatment of PAD, explore our comprehensive care approach, which is designed to optimize outcomes and enhance quality of life.
Conclusion
Peripheral arterial disease is a serious condition that requires careful management to prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes. While PAD itself is not typically fatal, it significantly increases the risk of arterial events and can lead to severe limb complications if left untreated. The key to improving the prognosis of PAD lies in early detection, proactive management, and a commitment to making healthy lifestyle choices.
By understanding the risks associated with PAD and taking steps to manage the condition, you can reduce your risk of complications and live a healthier, more active life. If you have been diagnosed with PAD or are at risk, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. To learn more about how we can help you manage PAD and enhance your arterial health, visit our arterial treatment page.
With the right care and management, PAD is a condition that can be effectively controlled, allowing you to maintain your quality of life and reduce the risk of serious complications.