The way we work, live, and engage with the designed world will all be drastically altered by artificial intelligence (AI), a disruptive force. It is now considered a novel technology. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing numerous industries and surpassing previously perceived limits due to its capacity to analyze vast quantities of data, draw lessons from past experiences, and make judgments. This article looks at artificial intelligence’s present situation, its uses in many industries, and its possible future effects.
Artificial Intelligence Evolution
Since its inception, AI has advanced significantly. Science fiction served as the initial inspiration for artificial intelligence (AI), which has advanced quickly in recent years. Rule-based systems, in which machines were explicitly programmed with instructions, were the main focus at first. However, the true breakthrough has been made possible by machine learning, which enables algorithms to learn from information and gradually enhance performance.
The game has changed due to machine learning, particularly deep learning. Advances in machine learning for language processing, image and audio acceptance, and even making intelligent choices have been fueled by neural networks, which draw inspiration from the human brain. The availability of massive amounts of data, strong computing resources, and cutting-edge algorithms is speeding up the creation of AI.
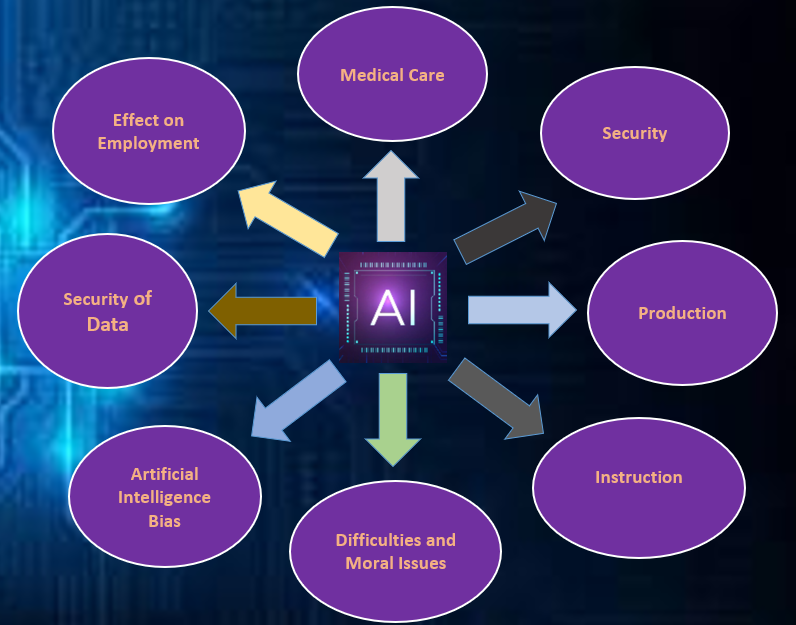
Medical Care:
AI is transforming patient care, diagnosis, and treatment planning in the medical field. Machine learning algorithms are used to evaluate medical images, such as MRI and X-ray images, and identify anomalies with a level of precision that surpasses human capability. AI is also employed to tailor medical care based on a person’s genetic characteristics, enhance treatment regimens, and forecast illnesses.
Security
AI is enabling the identification of fraud, risk control, and enhanced customer service in the banking sector. Utilizing machine learning examples, algorithmic trading is able to evaluate market developments and perform trades at a speed that is not feasible for human traders. Natural language processing-powered robots and AI-powered assistants enhance consumer interactions by offering tailored advice and assistance.
Production
AI is automating, improving quality control, and predicting maintenance in manufacturing processes. AI-powered solutions are used in “smart factories” to anticipate equipment breakdowns, minimize downtime, and boost operational effectiveness. Robots with AI algorithms enhance industrial processes’ accuracy and flexibility, which raises the caliber of the final product.
Instruction
AI is essential to individualized learning in the classroom. Artificial intelligence (AI) is used by adaptive learning platforms to evaluate each student’s progress and modify the curriculum as necessary. Smart teaching solutions give students immediate feedback and support to help them master complex subjects.
Difficulties and Moral Issues:
While AI has numerous advantages, there are also serious drawbacks and moral dilemmas. Concerns about employment, privacy, and potential prejudice in AI systems must all be addressed. Robust regulatory frameworks are becoming more and more necessary to assure responsible creation and use of AI systems, as these systems become more autonomous and complex.
Artificial Intelligence Bias:
A major obstacle in the development of AI is the possibility of bias in algorithms. When artificial intelligence (AI) systems learn from historical data, their models may reinforce or even perpetuate biases found in the data. This is particularly true for facial recognition technology, where racial and gender prejudice is present in the algorithms. It will take ongoing work to include transparency in algorithmic decisions, diversify datasets, and provide ethical norms for developers in order to combat bias in AI.
Security of Data:
A greater dependence on AI will necessitate the gathering and processing of enormous volumes of data. This gives rise to worries regarding personal data exploitation and privacy. One of the biggest challenges is striking a balance between safeguarding people’s privacy and using data to enhance AI. In an effort to allay these worries, regulatory frameworks like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) set standards for the moral management of personal data.
Effect on Employment:
As AI technology develops, worries about how it can affect jobs are becoming more and more prevalent. Certain employment may be replaced by automation and AI-driven systems, which could result in labor displacement. Nonetheless, it’s critical to acknowledge AI’s potential to enhance current roles and open up new ones. Programs for retraining and upskilling workers are crucial for preparing them for the rapidly evolving nature of the workforce.
Artificial Intelligence’s Future Prospects:
AI has a bright future ahead of it, but it also presents many obstacles. These are some of the main areas where AI is anticipated to make a significant impact as technology develops:
Autonomous vehicles:
The future of AI applications is represented by the development of self-driving automobiles. Here’s an illustration. Vehicles with AI-powered systems can perceive their environment, react quickly, and drive safely. Self-driving car adoption on a large scale has the potential to completely transform transportation by lowering accident rates and increasing productivity.
Progress in Medical Science:
AI will lead to more advancements in healthcare, such as remote patient monitoring, drug research, and tailored therapy. Large datasets are analyzed by AI algorithms to find patterns that result in more specialized and efficient treatments. AI-driven remote monitoring tools enhance patient outcomes and allow for proactive health interventions.
AI and Quantum Information technology:
AI and quantum computing have a promising synergy. Because quantum computers can do complicated computations at previously unheard-of rates, they can greatly enhance the training and optimization of AI models. The combination of AI and quantum computing may create new avenues for the solution of challenging issues that are presently outside the purview of traditional computers.
Explainable AI: Filling the Knowledge and Trust Gap
Because complicated models are typically opaque, this presents a significant barrier to the general use of AI. The goal of explainable AI (XAI) is to solve this issue by increasing the transparency of AI systems’ decision-making processes. Understanding and being able to interpret AI’s outputs becomes crucial as it grows in complexity. In addition to increasing user and stakeholder trust, explainable AI also helps detect and lessen bias, increasing the accountability and social responsibility of AI systems.
Frontier Computing and AI: Revolutionizing Responsiveness and Computing Power
The processing and analysis of data will be altered by the combination of cutting-edge technology and AI. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing seeks to lower latency and enhance real-time decision-making. In applications where quick response is crucial, like the Internet of Things (IoT) and autonomous devices, this synergy is extremely beneficial. AI and edge computing interact together to improve system responsiveness and efficiency, which raises the bar for smart device functionality and overall performance.
AI in Innovation: Unlocking Generative Models’ Potential
AI has an impact on creativity as well since models that generate push the limits of what machines are capable of producing. Artistic and visually appealing content can be produced by AI algorithms; this is evident in everything from music and art to literature and design. An important factor in this growth is the emergence of generative adversarial networks (GANs), which enable AI systems to pick up on and mimic artistic techniques, creating new avenues for human-machine cooperation in the creative process. Openness to sexuality emerged.
Ethical AI Management: Creating the Conditions for Conscientious AI Research
Ethical governance is becoming more and more necessary as AI technologies advance. Establishing a structure for the conscientious advancement and application of artificial intelligence is necessary in order to fairly distribute the advantages and mitigate any possible drawbacks. Transparency, responsibility, and inclusivity in AI decision-making processes are all part of ethical AI governance. In order to guard against unforeseen outcomes as AI develops, policymakers, business executives, and engineers must collaborate to develop and execute laws that give justice, privacy, and ethical issues first priority.
AI and Weather Change: The New Era in Environmental Technology
Artificial Intelligence is showing promise as a potent tool to address environmental issues and advance sustainability as the globe struggles with the effects of climate change. AI applications are utilized to create predictive models for climate-related occurrences, optimize energy use, and enhance resource management. AI’s ability to support sustainable behaviors and lessen the consequences of climate change is seen in everything from smart energy grids to precision agriculture. This underscores AI’s position as a revolutionary force to create a greener future.
International Cooperation in AI Research: Promoting Creativity and Information Exchange
Artificial Intelligence is a rapidly evolving discipline that gains from international cooperation and knowledge exchange. In order to solve complicated problems, ensure responsible growth of AI technologies, and speed up AI discoveries, international cooperation among institutes, researchers, along with business leaders is imperative. Working together makes it easier to share different viewpoints, knowledge bases, and resources, which fosters a synergistic atmosphere that advances AI innovation. Promoting international cooperation is becoming more and more important as AI develops in order to solve global issues and maximize AI’s beneficial effects on society.
Conclusion
In the exploration of artificial intelligence, Harish Munigala emerges as a pivotal figure, shedding light on the complexities and transformative potential of AI technology. Through his insights and contributions, we grasp the profound impact AI has on various sectors, from healthcare to automation, and the ethical considerations it brings to the fore. Munigala’s work highlights the importance of responsible innovation and the need for continuous dialogue between technology creators, policymakers, and the public to ensure AI serves the greater good. His perspective reinforces the idea that AI, when guided by human wisdom and ethical standards, can significantly enhance our capabilities, foster growth, and address some of the most pressing challenges facing society today.